Cities that want to build transit ridership in an era of major declines should pay far more attention to the weakest link: bus service.
That advice comes from a new analysis of 2018 ridership data by TransitCenter, which shows that the seven cities that managed to grow transit ridership last year had either expanded bus service or completely overhauled their bus system in recent years.
Three of those cities — Seattle, Houston and Austin — reorganized their bus systems substantially in order to expand frequent service in the last few years. (Seattle also greatly expanded total bus service). Meanwhile, San Antonio, Las Vegas and Pittsburgh all added substantial bus service since 2013, TransitCenter reports. And Detroit has expanded frequent service on its 10 busiest bus routes, adding about 500 trips a week.
"In almost every American city, bus service carries the majority of trips, so it should be no surprise that cities have to improve bus service to grow ridership," TransitCenter staff wrote in a blog post.
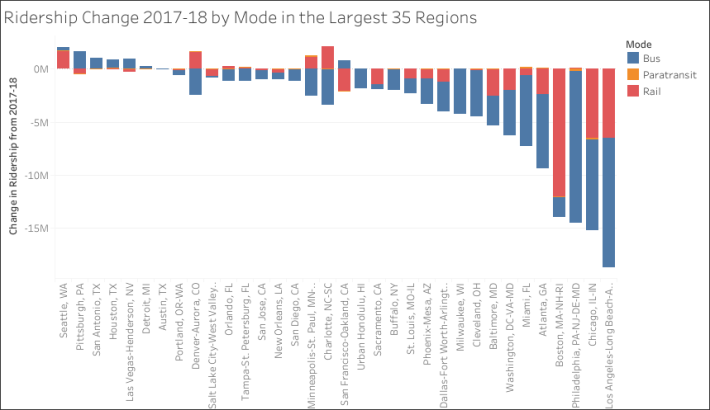
Most large cities with legacy rail systems with backlogs of maintenance are still struggling to check the decline in ridership, which is also affected by low gas prices and a deluge of underpriced Uber and Lyft cars. Among big cities, San Francisco seems to be performing the best. TransitCenter credits the city for improving bus ridership by adding all-door boarding, which speeds up bus journeys, across the city. As a result, all of the city's gains were in bus ridership, even as the overall transit population declined.






