The owners of the largest passenger cars on the road actually drove more in 2020 than they did in 2019, according to new data that can also explain why road deaths surged so sharply during the early days of the pandemic.
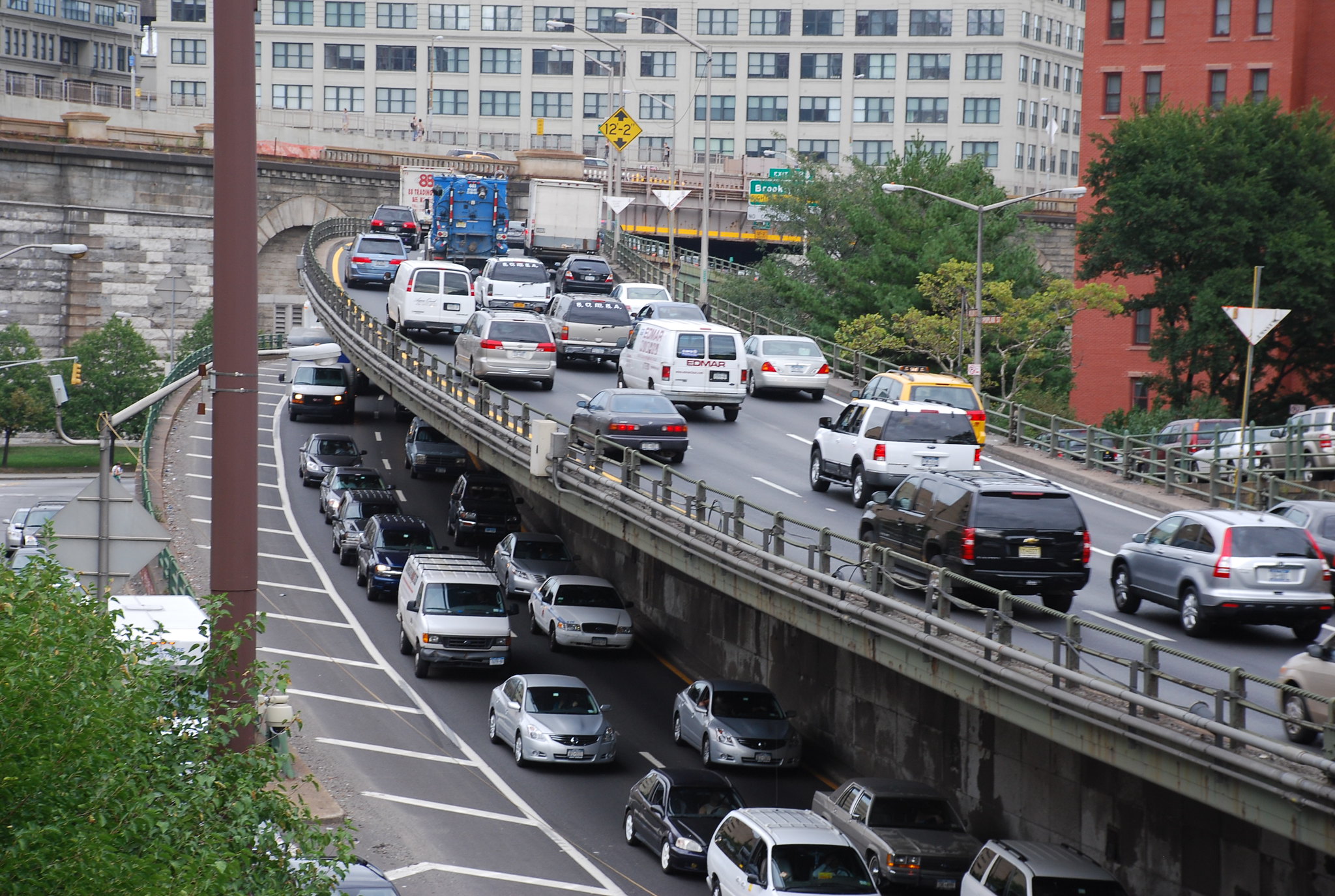
According to estimates from the Federal Highway Administration, vehicles classified as "light truck, long wheelbase" — a category which includes many of America's most popular pick-up trucks, or any car with at least 121 inches between its axles — were driven about 1.5 billion miles more during the year that much of the country fell under quarantine orders than they were the year before, an increase of about one percent.
That vehicle classification doesn't include many of the most common SUVs on the road (though monster models definitely exist in the sport utility market), but it does include the three best-selling new car models in 2020: the Ford F-Series, the Chevy Silverado, and the Dodge Ram, all of which are pick-ups. The rising popularity of both SUVs and light trucks has long been recognized as a significant factor in the nation's rising pedestrian death rate, which surged 21 percent between 2019 and 2020, the largest annual increase ever recorded by federal agencies; light trucks of all lengths are two to three times more likely to kill a walker in the event of a crash, because of their weight, height, and front-end design.
The total vehicle miles traveled among the nation's fleet of smaller cars in 2020, by contrast, was 16 percent lower than the total mileage recorded among bigger trucks. Person miles traveled, though, were significantly higher among smaller cars' drivers and passengers, suggesting that truck occupants were less likely to carpool.
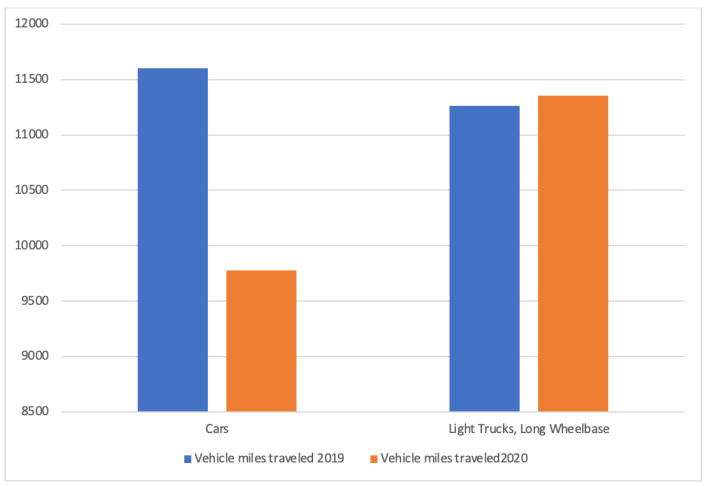
Researcher Michael Spivak, who first isolated these alarming stats for the Green Car Congress blog, hypothesized that pick-up drivers took to the road more because "telecommuters are more likely to drive a car than a light truck, and that the opposite is the case for non-telecommuters."
Earlier research, though, suggests a more complex picture.
Despite the enduring stereotype of pick-up truck drivers as rugged tradespeople working the nation's farms and building sites, market research has shown that less than 15 percent are actually employed in such industries, at least among the segment of drivers who bought their cars when they were new.
Moreover, in 2019, the average annual household income of pick-up owners was $108,334 — a number that likely rose as truck prices soared during the pandemic. In many cities, that puts light-duty truck owners squarely within the demographic that was most likely to be able to work from home during the early days of quarantine, rather than the least. Pick-up buyers are also disproportionately likely to be White, another group that was more likely to have access to telecommuting options, in contrast to Black and Latinx commuters, who became the majority of transit users during the pandemic.
It's theoretically possible, of course, that used pick-up owners were the ones driving up VMT totals for the whole light-truck market, and that they rarely left home except to perform essential labor. A simpler explanation, though, lies at the confluence of two well-established trends: that Republican voters are significantly more likely to buy the biggest cars on the market, and the are also significantly more likely to disregard public health officials' recommendations to stop the spread of COVID-19.
One study, for instance, found that GOP-leaning counties exhibited 14 percent less physical distancing between March and May 2020 than their Democrat counterparts, even after the researchers adjusted for the percentage of residents employed in essential industries like agriculture, as well as local quarantine orders that shut down shops and restaurants wholesale.
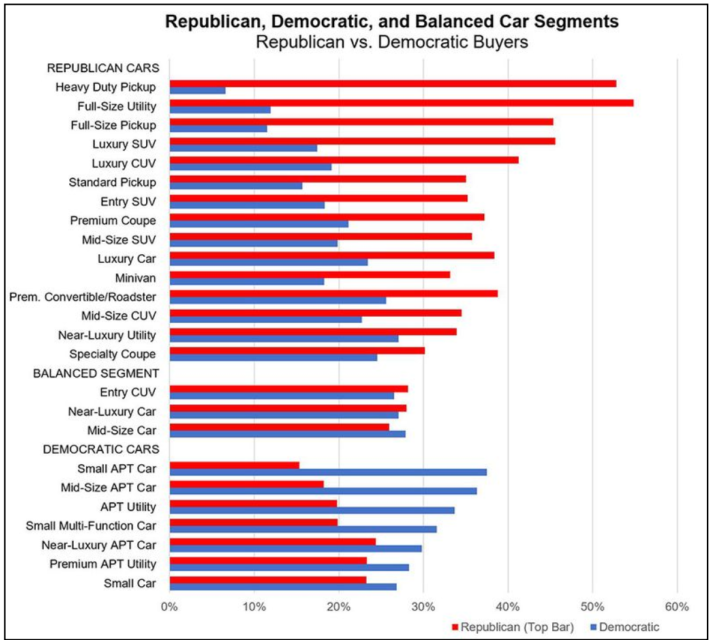
Whatever the reason why so many megacar drivers took to the road in 2020, there's no doubt that those motorists posed an outsized danger to vulnerable road users — and that something must be done about it.
The federal Department of Transportation faced criticism last week when the "safe vehicles" section of its National Roadway Safety Plan failed to commit to any new rule-making aimed at addressing swelling vehicle weights, towering hood heights, or flat-nosed front body designs, all of which experts say could help pedestrians' chances of survival when they are struck.
Until that happens, there's a good chance the proportion of light trucks in the vehicle fleet and the amount of time they spend on the road will keep increasing, too — and so will the death toll.






