Utah just enacted the most aggressive standard for drunk driving in the country, lowering the legal blood-alcohol limit to .05 percent.
The change, which took effect Dec. 31, was championed by State Rep. Norm Thurston, a Republican of Provo, told a local radio show, "it sends the message that in our state we don't want you to drink and drive."
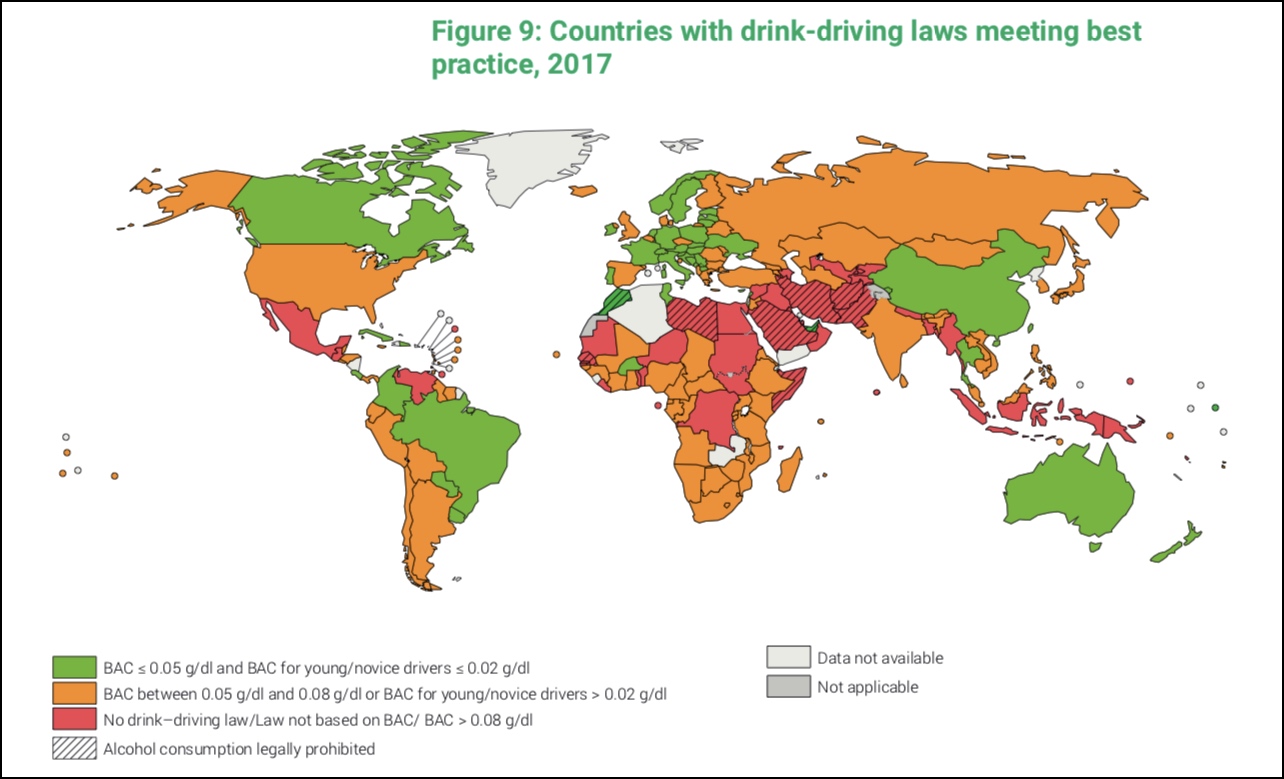
The National Transportation Safety Board has been urging states to lower the BAC limit — which was .08 in every state — for a little over a year, calling it one of its "most wanted" transportation safety improvements in 2017 and 2018 [PDF] because impairment begins well below .08. For those with a BAC between .05 and .08 the risk of a fatal crash is seven times greater, according to Dr. Bella Dinh-Zarr, vice chairwoman of NTSB. The average 165-pound man would still have to drink between two and three drinks to reach a BAC of .05, which takes three hours to fully dissipate.
Washington and Hawaii have also introduced bills lowering BAC limits to .05 at the agency's urging. Drunk driving still killed 10,500 Americans in 2015. But that only includes drivers with a BAC over .08. An additional 1,800 people were killed in crashes in which the driver had a BAC between .05 and .08, NTSB reports.
Nevertheless, Thurston is being attacked by "beverage industry" lobbyists and other critics, like Salt Lake Tribune columnist Robert Gehrke.
But the Utah legislature was right to ignore them. Every other peer nation in the world already imposes a .05 threshold, the World Health Organization said, as Streetsblog reported. Those nations all have dramatically lower per-capital traffic fatality rates.
Canada, for example, has a .05 BAC limit and also imposes stricter penalties on those who are caught violating the laws, according to Neil Arason, director of injury prevention and healthy settings at the British Columbia Ministry of Health. Stricter rules are one key reason Canada's per capita traffic death rate is about half the U.S.'s, Arason says. Alcohol-related fatal crashes declined 40 percent in British Columbia, for example, after the providence instituted stricter drunk driving laws in 2010.