Turns out paying people to buy cars isn't a great policy for the economy or the environment. That's the determination of a pair of Brookings Institution researchers who evaluated the effectiveness of the 2009 Cash for Clunkers program.
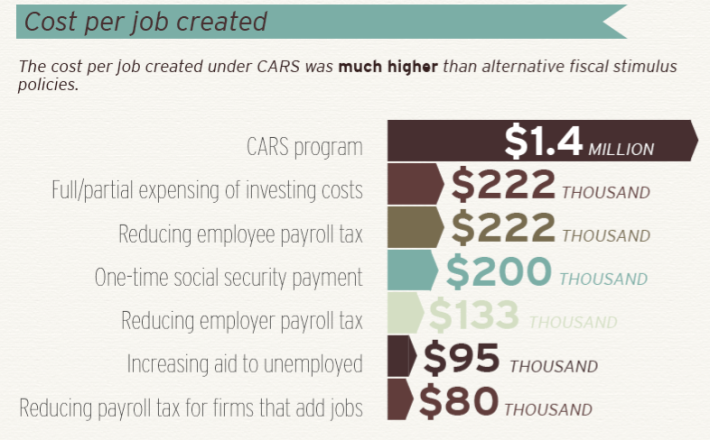
The $2.85 billion program, part of President Obama's economic stimulus package, produced only 2,050 "job-years," according to researchers Ted Gayer and Emily Parker. That means every year of employment attributed to it cost taxpayers about $1.4 million -- a far worse cost-benefit ratio than many other stimulus programs.
Between June and September 2009, about 700,000 people took advantage of the program known formally as the Car Allowance Rebate System (get it?). The federal government gave each participant a rebate between $3,500 and $4,500, depending on the estimated emissions reduction compared to the purchaser's previous car. New vehicles purchased averaged about 25 miles per gallon, compared to an average of about 16 m.p.g. for trade-ins.
However, Brookings determined that of these sales, only about 380,000 were a direct result of the program; the other 320,000 participants would have purchased cars during that time period anyway. And even many of the stimulated sales would have occurred during the following months without any subsidy, researchers determined.
"The net result was a negligible increase in GDP, shifting roughly $2 billion into the third quarter of 2009 from the subsequent two quarters," said Gayer and Parker.
Cash for Clunkers' environmental returns were less than stellar as well. The program resulted in reduced carbon emissions of between 9 and 28 million tons, at a cost of $91 to $301 per ton.
"The cost per ton of carbon dioxide reduced by the CARS program far exceeds the estimated social cost of carbon, suggesting it is an inefficient approach to reducing emissions," Gayer and Parker write. The cap-and-trade proposal rejected by the Senate in 2009 would have been far more meaningful, they add.
Cash for Clunkers produced similar environmental returns to the electric vehicle subsidy -- which, we've reported before, is not such a great use of tax dollars either.
At the time Cash for Clunkers passed, Washington failed to enact a less-expensive, $2 billion proposal to help preserve transit service for millions of Americans.





