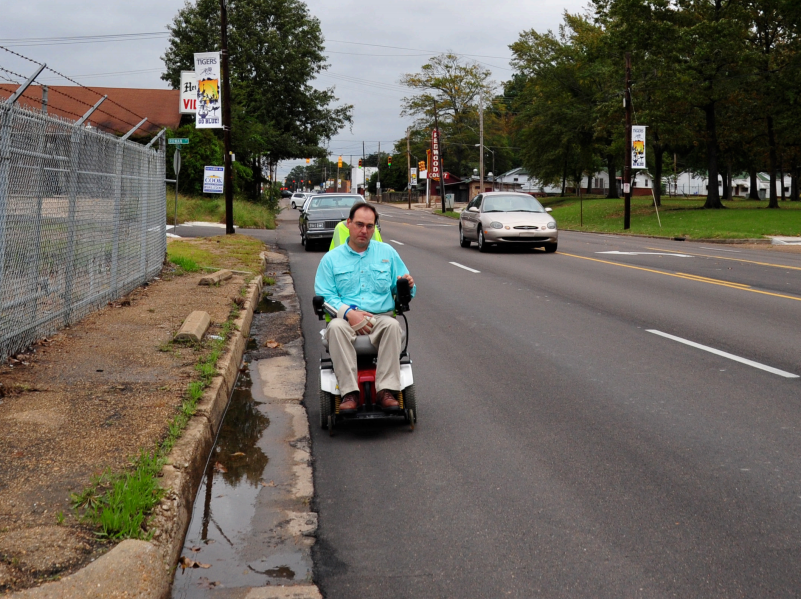
The 34-year-old Americans With Disabilities Act may soon — finally — give pedestrians, people in wheelchairs or parents pushing strollers true equality in the public right of way.
Late last month, the U.S. Department of Transportation signaled that it would adopt a bureaucratic mouthful: Accessibility Guidelines for Pedestrian Facilities in the Public Right-of-Way (also known as PROWAG) that were proposed a full year ago by the U.S Access Board.
If finalized, this proposed adoption will improve accessibility for pedestrians in the public right-of-way — a goal of the ADA, which was signed into law in 1990.
To understand how long this rule has been in the making, let's first review the history of the ADA and PROWAG with a nice, handy graphic:
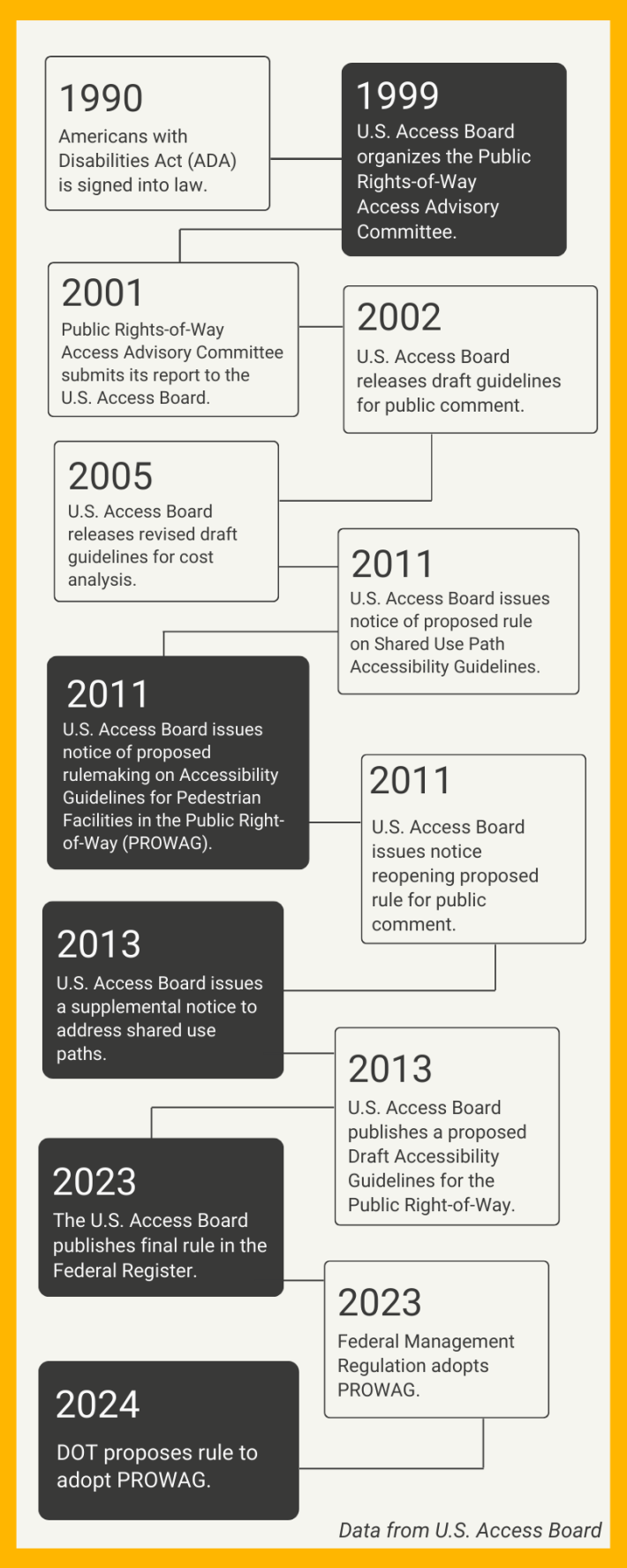
Reviewing the timeline, it's clear that accessibility in the public realm hasn't been much of a consideration after the passing of the ADA. For instance, it took nine years after the passing of the ADA for even a committee on the subject to be formed.
It would be another decade before the U.S. Access Board would publish the proposed accessibility guidelines for pedestrian facilities in the public right-of-way (PROWAG).
And last year, a final rule was published.
Now, a year later, this final rule is finally being proposed for adoption by the U.S. DOT.
Why it matters

For years, ADA has been the regulation, and PROWAG has merely been considered "best practice" for designers, who could choose whether to comply.
Meanwhile, the Centers for Disease Control states that 61 million adults in the United States live with a disability — roughly one-fifth of the adult population. The adoption of PROWAG could put to rest over 30 years of inequality when it comes to navigating the public realm for so many people.
Those experiencing disabilities, and those advocating for people with disabilities, have wanted equality and access since before the ADA was even written.
But the ADA only provided equality and access in one realm of public spaces: mostly buildings. PROWAG will finally give everyone accessible pedestrian facilities, including sidewalks, curb ramps, pedestrian signals, cross walks, detectable warning surfaces, on-street parking, transit stops, and more. The adoption of these guidelines for accessible pedestrian design will be life-changing for so many people in the way they are able to more independently get around the cities they live in.
Some of the simplest things that many people take for granted, such as having a sidewalk to travel on and a ramp to be able to access that sidewalk, or having a cross walk to cross the street and an audible push button to know when it is safe to cross, can make a huge difference in people’s lives.
Challenges to implementation
Although PROWAG will apply to all pedestrian infrastructure in the public right-of-way, it only applies to new construction, alterations or additions to past construction.
It does not include all existing infrastructure unless it involves new construction. Therefore, the implementation of PROWAG will most likely play out slowly over time as old infrastructure is replaced. Until that happens, there will continue to be outdated and non-compliant infrastructure.
Looking forward
Nonetheless, the adoption of PROWAG would ensure that accessibility will no longer merely be best practice, but rather, the new minimum required design. As such, it would make inequality illegal when it comes to accessibility for pedestrians.
With PROWAG the legal regulation, engineering designs will be required to meet certain specifications with infrastructure, such as curbs at least four inches high, slopes not steeper than 1:2, and audible and vibrotactile walk indications at crosswalks.
These minor specifications will create a major impact in people’s lives.
Although it has been a long time coming, and might still be a slow start, the adoption of PROWAG will day by day make life easier for not even just those with disabilities. The accessible infrastructure provided by PROWAG would benefit all people, including those traveling with suitcases, parents with strollers, young children, the elderly, and so many more.
The adoption of PROWAG will make history; it is yet another step forward in the fight for equality for all.
The U.S. DOT will be taking comments on the final rule until Sept. 23, 2024. There are multiple ways to comment, but each must include the DOT docket ID DOT-OST-2024-0090:
- Submit a comment through the Federal eRulemaking Portal by clicking here.
- Send a snail mail comment to:
- Docket Management FacilityU.S. Department of Transportation1200 New Jersey Avenue SE, Room W12-140Washington, DC 20590-0001.
- Fax a comment to 202-493-2251






