This article is a part of our annual Highway Boondoggles series, in partnership with U.S. PIRG. This series will explore some of the worst planned highway projects across the country, and explore why they deserve to be cancelled — and why U.S. transportation policy must be reformed to discourage similar initiatives in the future. Learn more about the other boondoggles that made this year's list by clicking here. You can also view the full report here.
I-35 Reconstruction, Duluth, Minn.
Cost: $510 million+
It’s sometimes said that Minnesota has two seasons: winter and road construction. In Duluth, an ongoing, multiyear highway project has sucked up millions of taxpayer dollars on a road that many residents believe shouldn’t even be there in the first place.
Duluth is the northern endpoint of the 1,569-mile-long Interstate 35. When I-35 was built, half a century ago, it was envisioned as a major route to the Canadian border. However, it now only travels a short distance beyond downtown Duluth before ending abruptly just north of the city. On its way, it slices Duluth’s downtown in two with a mass of roadway infrastructure that makes up the Twin Ports Interchange connecting I-35, I-535 and U.S. Highway 53.
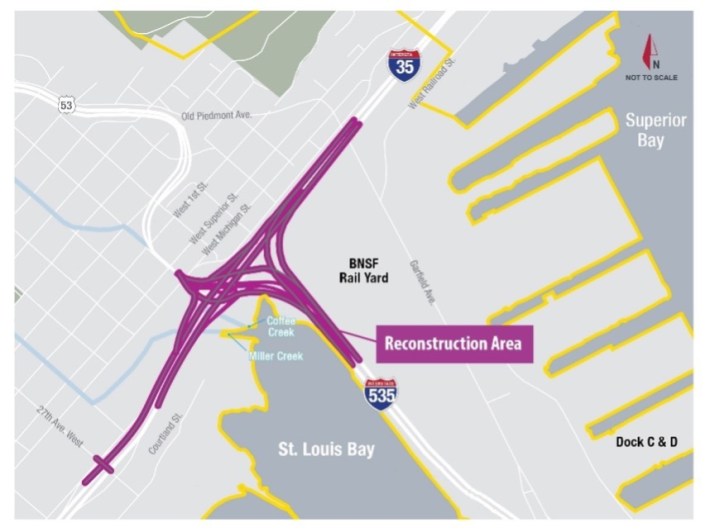
Known locally as the “Can of Worms,” the interchange was built in the 1960s and ’70s, and, according to Minnesota Department of Transportation, carries an average of 80,000 vehicles per day, 5,320 of which are heavy commercial traffic like trucks and buses. Now aging and riddled with safety issues, the interchange is getting a major rebuild. According to MnDOT, this reconstruction will “enhance safety by eliminating blind merges and left exits, replace aging infrastructure, and better accommodate freight movements.” The project was originally estimated to cost $343 million.
True to its name, however, the Can of Worms was already $100 million over budget before construction even began, with soil and water contamination and various other issues at the site ramping up the costs to $442 million and forcing MnDOT to put sections of the project on hold so as to remain within its currently stated $343-million budget. However, in June 2022, local media reported that IIJA funding has enabled MnDOT to press ahead with the on-hold sections of the project, adding an estimated $167.7 million to the existing price tag.
The Twin Ports Interchange is the opening salvo in a series of major I-35 reconstruction projects anticipated over the coming years. The Duluth Metropolitan Interstate Council notes that while planning and design for further work on the I-35 corridor in the area has not yet been done, and the exact scope of these projects not yet known, it is “fully anticipated” that work will go ahead within the lifetime of the current Duluth-Superior Long Range Transportation Plan. That plan notes that the costs involved will exceed the projected revenues of MnDOT District 1 and WisDOT Northwest Region and likely require additional funding from “statewide sources” or elsewhere.
Although ostensibly well-intentioned in its stated objective — to replace aging infrastructure and improve safety — questions remain over whether reconstruction of the Twin Ports Interchange and other planned projects along the I-35 corridor are a justifiable use of public money, or whether they are simply a diversion of much-needed funds into prolonging the life of a road that many local residents believe should be removed altogether.
According to Duluth Metropolitan Interstate Council’s Sustainable Choices 2045 transportation plan, I-35 through Duluth now handles less than 50 percent of its intended capacity. Over the last two decades, traffic on the downtown stretch of the highway has decreased by 35 percent, from 48,900 daily trips in 1998 to 32,000 in 2015. And many local residents see little benefit from the road: 32 percent of people living within a mile of the downtown stretch of I-35 don’t own a car, and yet I-35, Railroad Street and associated infrastructure occupy a total of 44 acres of land in downtown Duluth – a little under 20 percent of all space in the downtown area. While massive amounts of public money are being spent on the I-35 reconstruction, the city’s streets are in many cases in desperate need of maintenance and repair, and other highway infrastructure projects in the city have gone substantially over budget.
Moreover, pouring money into extending the life of I-35 runs counter to the city’s own Imagine Duluth 2035 plan, adopted in 2018 as the framework for future decision-making in the city. The plan, which “puts people and natural places at its center, and shifts away from the auto- and industry-centric development of the past,” includes “reduc[ing] infrastructure costs through innovation and wholesale design change” and “improv[ing] system condition and connections in and between downtown and Canal Park [Duluth’s main vacation and entertainment hub],” as well as enhancing multi-modal travel options and basing decisions about transportation infrastructure primarily in the context of “improving city and neighborhood vitality, and not solely on automobile through-put.”
It is difficult to see how the millions of dollars being spent on I-35 reconstruction furthers any of these goals.
These expenditures are also out of step with many Duluth residents’ desire for a more varied, multimodal transportation system. A 2019 survey by Duluth-Superior Metropolitan Interstate Council found that a substantial majority of respondents believe their transportation system should prioritize multiple modes of travel, including walking, biking and transit. Of the respondents, 66% voiced a preference for a multimodal system and 45 percent strongly so. Those favoring such a system supported the idea of reducing auto-oriented infrastructure to facilitate such a system, with only 21 percent of respondents advocating for prioritizing cars. Forty-three percent of respondents said that if certain key barriers were removed — including sidewalks in poor condition or absent altogether, and unsafe crossings — they would walk more.
Likewise, 35 percent of all respondents said that if safety and other key issues were addressed, they would bike more, with almost a quarter of those who never cycled saying they would do so if such barriers were removed.
In 2021, recognizing that the freeway “may not be in line with the goals of the community,” Duluth’s city council unanimously adopted a resolution to re-evaluate I-35 and examine alternative visions for the I-35 corridor in downtown Duluth. The outcome of that evaluation remains to be seen. In the meantime, as of August 2022, the can of worms remains open.