How can cities make more efficient use of street space, so more people can get where they want to go?
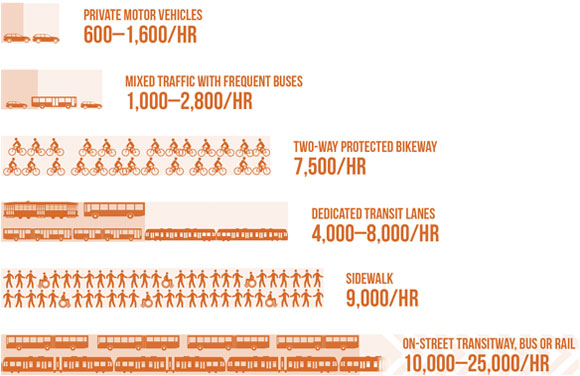
This graphic from the new NACTO Transit Street Design Guide provides a great visual answer. (Hat tip to Sandy Johnston for plucking it out.) It shows how the capacity of a single lane of traffic varies according to the mode of travel it's designed for.
Dedicating street space to transit, cycling, or walking is almost always a tenacious fight, opposed by people who insist that streets are for cars. But unless cities make room for pedestrians, cyclists, and transit riders, there's no room for them to grow beyond a certain point.
NACTO writes:
While street performance is conventionally measured based on vehicle traffic throughput and speed, measuring the number of people moved on a street -- its person throughput and capacity -- presents a more complete picture of how a city’s residents and visitors get around. Whether making daily commutes or discretionary trips, city residents will choose the mode that is reliable, convenient, and comfortable.
Transit has the highest capacity for moving people in a constrained space. Where a single travel lane of private vehicle traffic on an urban street might move 600 to 1,600 people per hour (assuming one to two passengers per vehicle and 600 to 800 vehicles per hour), a dedicated bus lane can carry up to 8,000 passengers per hour. A transitway lane can serve up to 25,000 people per hour per travel direction.
Of course, it usually takes more than changing a single street to fully realize these benefits. A bike lane won't reach its potential if it's not part of a cohesive network of safe streets for biking, and a transit lane won't be useful to many people if it doesn't connect them to walkable destinations.
But this graphic is a useful tool to communicate how sidewalks, bike lanes, and transitways are essential for growing cities looking to move more people on their streets without the costs and dangers inherent in widening roads.





