If you want to increase cycling safety in your city, drop the helmet law and focus on getting more people-- particularly women -- on bikes, with street designs that offer separation from vehicle traffic.
That's the finding of a new study by researchers at the University of British Columbia [PDF] evaluating safety outcomes for cyclists across Canadian provinces and territories.
Lead author Kay Teschke and a team of researchers looked at cyclist injuries requiring hospitalization in 10 Canadian provinces and three territories between 2006 and 2012. They checked to see if hospitalization rates were linked in any way to helmet laws and cycling rates, and they checked for variations in hospitalization rates by sex and age.
Helmet laws were found to have no relationship to hospitalization rates. That was true even though self-reported helmet use is higher in areas of Canada that mandate it (67 percent) than in areas that don't (39 percent).
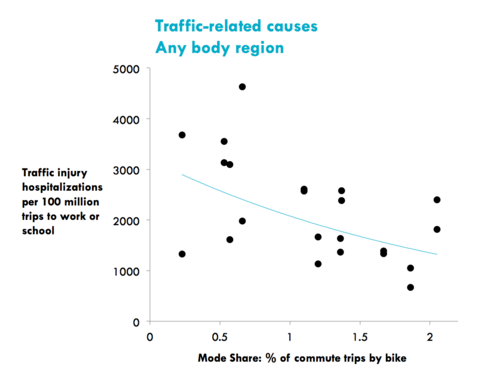
But having a higher rate of cycling in one's community does seem to have an impact on safety. Using Canadian government data on cycling activity, researchers found that men and woman were both less likely to be injured while biking in communities where more people bike.
It's not the first time this effect, sometimes called "safety in numbers," has been observed, though the researchers wrote in their summary of the study, "the explanation could also be 'numbers in safety' as safer bicycling infrastructure has been shown to attract more people to cycle."
The researchers also found that women were much less likely to be hospitalized for a cycling injury than men, echoing the results of other studies examining traffic collisions of all kinds. The authors attribute this to a "lower propensity for risk taking" among women.
"Transportation and health policymakers who aim to reduce bicycling injury rates in the population should focus on factors related to increased cycling mode share and female cycling choices," the authors conclude.





