When someone builds a new home, does it make the city stronger and more fiscally sound? Or does it drain public resources? The answer depends a lot on where it's sited and, more specifically, where it lies in relation to other homes and businesses.
Smart Growth America has developed a fiscal impact model that helps predict how developments will help or hurt the municipal bottom line. The tool they developed [PDF] takes into account how density affects the cost of delivering city services, from streets and sewers to fire protection, school busing, and garbage collection.
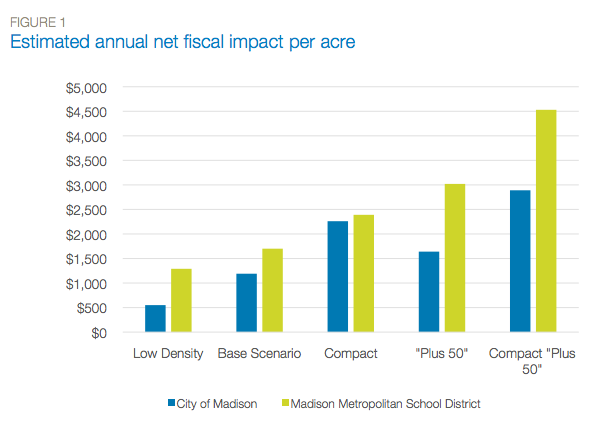
SGA applied its model to a proposed 1,400-acre development in Madison, Wisconsin, called Pioneer Square. Researchers varied the density and number of units across five development scenarios, ranging from "low density" (about two housing units per acre) to "Compact Plus 50" (about 7 units per acre).
According to SGA's model, the higher density development scenarios would have a far better effect on the city's budget [PDF]. Compared to the "low density" scenario, "Compact Plus 50" would generate 233 percent more revenue per acre for the city.
SGA says the results are actually conservative because the tool assumes higher-density properties will have lower taxable value, due to smaller lot sizes.
Unfortunately, most cities don't use very sophisticated methods to estimate the impacts of new housing developments. Instead, reports SGA, they assume each new home in the city will impose the same costs as the average home. That ignores all the variability in types of housing -- and could leave cities with big financial liabilities down the road.





