Who is most at risk of being hit by a car?
People on foot make up a growing proportion of people killed in traffic -- 15 percent in 2012, up from 11 percent in 2007. Children, seniors, and people of color account for a disproportionate share of the victims.
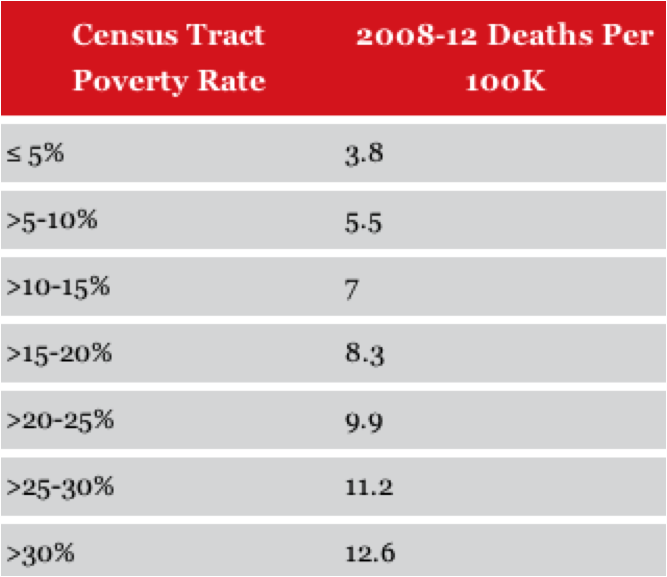
So do people living in low-income areas, according to a new analysis by Governing. A review of pedestrian deaths from 2008 to 2012 revealed that the fatality rate is twice as high in America's poorest neighborhoods as in higher-income neighborhoods.
Governing's Mike Maciag writes that efforts to improve walkability have often been centered in downtown areas and commercial districts while poor people, priced out of those neighborhoods, are moving into less walkable suburbs:
Bridging the Gap, a program of the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation, conducted field research assessing a sample of street segments in 154 communities in 2010. In high-income areas, 89 percent of streets had sidewalks, while only 49 percent did in low-income areas. Marked crosswalks were found in 13 percent of high-income areas, compared to just 7 percent of streets in low-income communities. The study found similar disparities for street lighting and traffic calming devices.
To some degree, people living in poor neighborhoods may be more at risk of being hit while walking because they walk more than people who can afford cars. But low-income neighborhoods are also more burdened by the legacy of car-centric street design than affluent neighborhoods. “Historically, many could not fend off construction of highways and major arterial roadways the way wealthier communities did,” Maciag writes.
Low-income neighborhoods that struggle with high crime rates may have the added problem of what former DC and Chicago DOT Commissioner Gabe Klein has called "a broken windows effect," whereby reckless driving and violent crime exacerbate each other. In places where violent crime rates are higher, the thinking goes, motorists are also less likely to observe the law, putting pedestrians at risk.
Add to that the evidence that drivers are less likely to slow down or stop for people of color and you have a recipe for gross inequity on our streets.