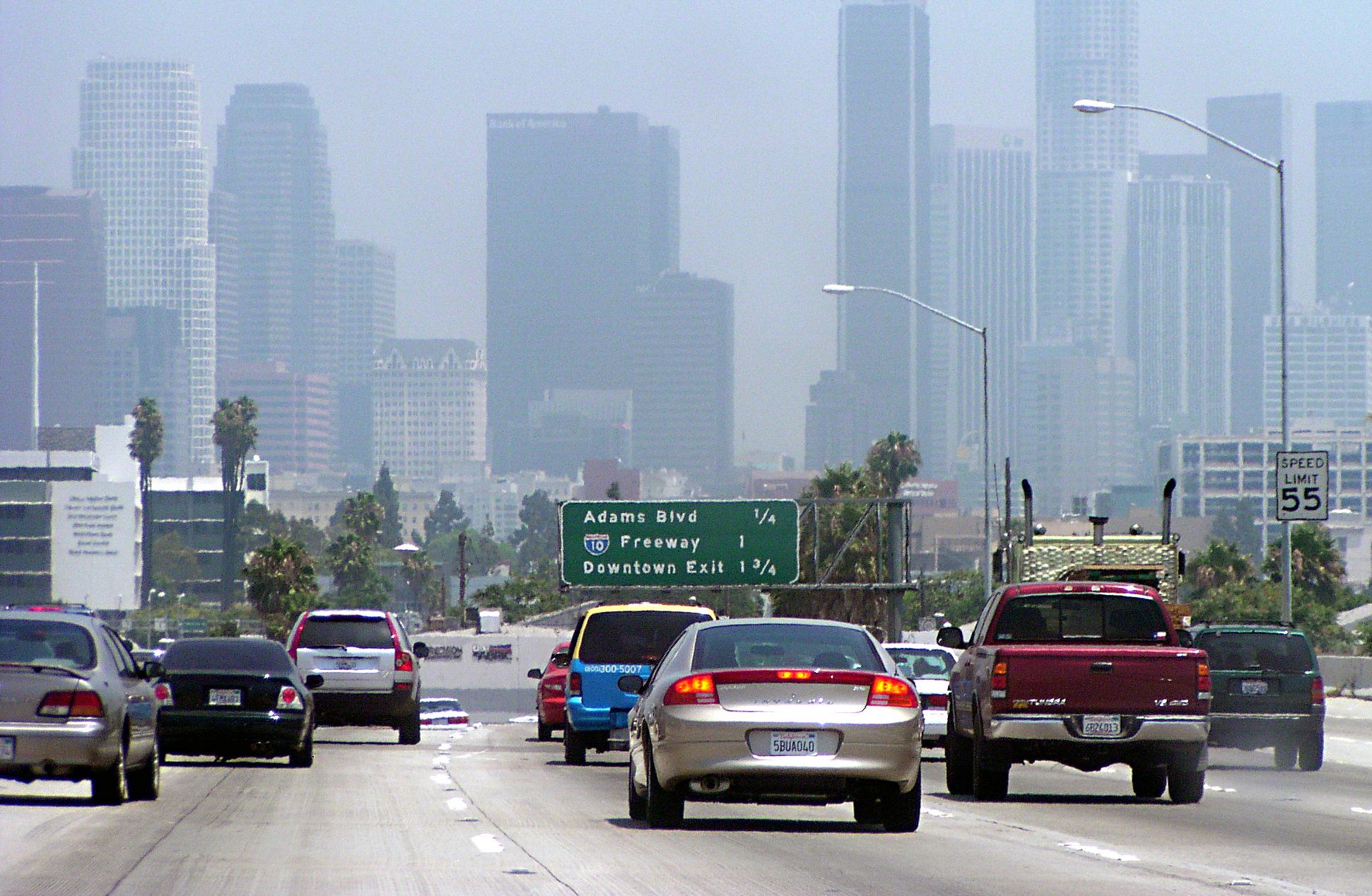
For decades -- through the rise of the two-car household, women entering the workforce, the growth of the exurbs -- Americans reliably put more miles on their cars every year.
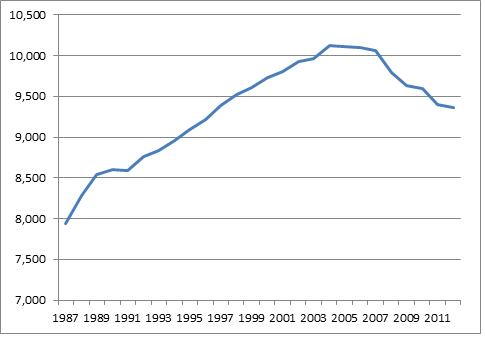
But no longer. Last year, for the eighth year in a row, vehicle miles traveled ticked down on a per-capita basis. The average American drove 37 fewer miles in 2012 than in 2011 -- a 0.4 percent drop, according to new data from FHWA. It's a small but significant decrease, continuing the downward slide of per-capita VMT that began in 2004, well before the economy faltered.
Experts attribute the reversal to a variety of factors including the gradual retirement of the baby boomer generation, volatile gas prices, decreased interest in driving by millennials, and the increasing popularity of walkable neighborhoods.
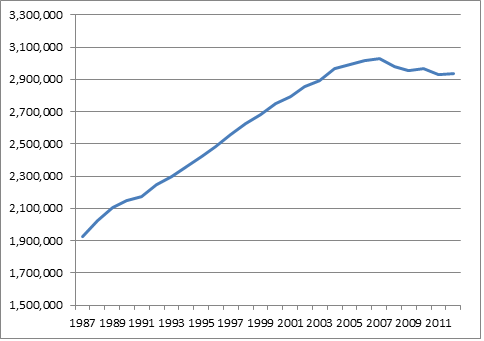
Meanwhile, population growth caused total mileage to tick up 0.3 percent in 2012. Total VMT, which has also seen a reversal of historical patterns, has declined three of the last eight years, for a net decrease of 0.9 percent over that time, reports the State Smart Transportation Initiative. Noting that total mileage has leveled off, SSTI advises state DOTs to rethink projects that add highway lanes -- projects that are often justified based on faulty models assuming growth in VMT.
Deliberate policy can have also a powerful impact on VMT patterns. In Portland, for example — a city that has recently done as much as any other to promote modes other than driving — vehicle miles traveled began decreasing in 1996 [PDF].