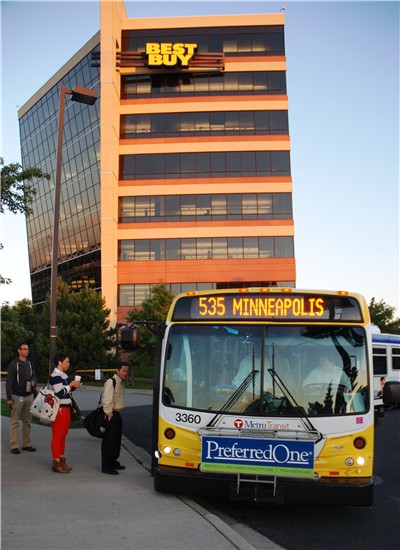
How to make transit work in sprawling suburbs is a difficult design problem -- but a couple small changes can have a big impact, according to new research from the University of Minnesota.
The team at the Accessibility Lab at the University of Minnesota modeled and measured job access both by transit and by car for those living near the Twin Cities' 114 Park-and-Ride transit stations under different scenarios. They found that two key infrastructure offerings -- park-and-ride lots combined with dedicated highway lanes -- can make transit substantially more competitive with driving in suburbia. The combination of those elements increases the relative number of jobs available within an hour trip by transit about 19 percent compared to driving.
The study helps support the case for "managed" highway lanes. In the Twin Cities, these lanes are reserved for carpoolers, buses and those who pay a special toll during rush hour. These lanes speed more efficient vehicles past traffic and provide an incentive not to drive to work alone. If they were applied across the entire twin Cities Metro, they increase the number of jobs available to the average suburban resident who lives within a half-mile of a Park-and-Ride station by 13 percent.
Park-and-Ride stations also help make unwalkable sprawling suburban areas more transit accessible, the study found. Suburban neighborhoods have low transit accessibility by foot in general, the study found. But when auto access to a park-and-ride station is factored in, it makes a big difference.
“Overall, PNR accessibility is three times greater than walk-up transit accessibility for the average Twin Cities worker," author Kristin Carlson said in a statement.
The Twin Cities uses currently uses managed lanes that allow buses on three highways at rush hour.