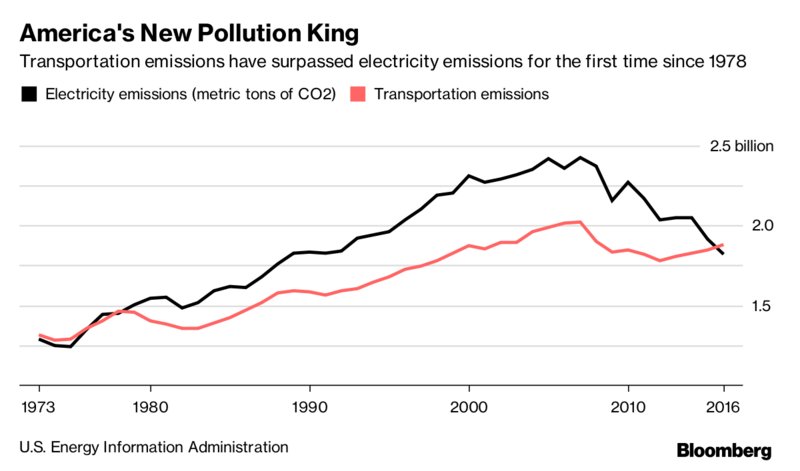
Toward the end of last year, the U.S. transportation sector surpassed electric power as the nation's largest source of greenhouse gas emissions. At Bloomberg, Tom Randall writes that the Trump administration's attack on fuel efficiency standards could slow down attempts to clean up transportation -- or progress could accelerate if the market for electric vehicles takes off.
But changing tailpipe emissions is just one avenue to reduce carbon from transportation. Changing the amount people drive is another, and it can have a powerful effect.
A new paper from Allen Greenberg of the Federal Highway Administration and John Evans from Cambridge Systematics makes a compelling case for reducing transportation emissions with three simple changes to driving incentives [PDF].
Cleveland-based air quality researcher Tim Kovach summarizes these recommendations on his blog:
- Converting fixed pricing mechanisms for car insurance to pay-as-drive-and-you-save (PAYDAYS), which charge people a variable rate, based upon how many miles they drive;
- Requiring employers who provide free parking for their employees to implement parking cash-out programs, which provides an equivalent cash incentive to employees who do not drive alone to work; and
- Converting fixed-percentage sales taxes on new vehicle purchases to mileage-based taxes spread over a three-year period.
The impact of changing these price signals could be substantial, achieving between 37 percent and 95 percent of the emissions reductions projected from the Obama administration's Clean Power Plan, the authors estimate.
We know the Trump administration doesn't care about global warming and is outright hostile to any attempts to address it. So Greenberg and Evans say states should pick up the slack.
Kovach explains:
They found that if each of the 19 states (plus the District of Columbia) that voted for Hillary Clinton in 2016 signed up for these three ideas, it would cut GHG emissions by 103 MMTCO2e (40% of total potential savings).
Next, they estimated that if California, the nine East Coast states in the Regional Greenhouse Gas Initiative (RGGI), and the eight other states that signed up to defend the CPP in federal court all took action, they could achieve 35% of the emissions savings from the CPP.
More recommended reading today: Green Caltrain reports on an analysis that reveals an equity problem with the way transit fares are structured. Greater Greater Washington takes a look at nine transit smart cards from around the U.S.