Tony Dutzik is a senior policy analyst with the Frontier Group. This article was originally posted on the Frontier Group's blog.
The U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA) -- the data and analytical wing of the Energy Department -- is out today with a fascinating analysis of changing driving trends and their implications for America’s energy future. The analysis, part of the EIA’s annual package of forecasts called the "Annual Energy Outlook," reviews recent changes in demographic, economic, technological and other factors affecting the number of miles Americans drive.
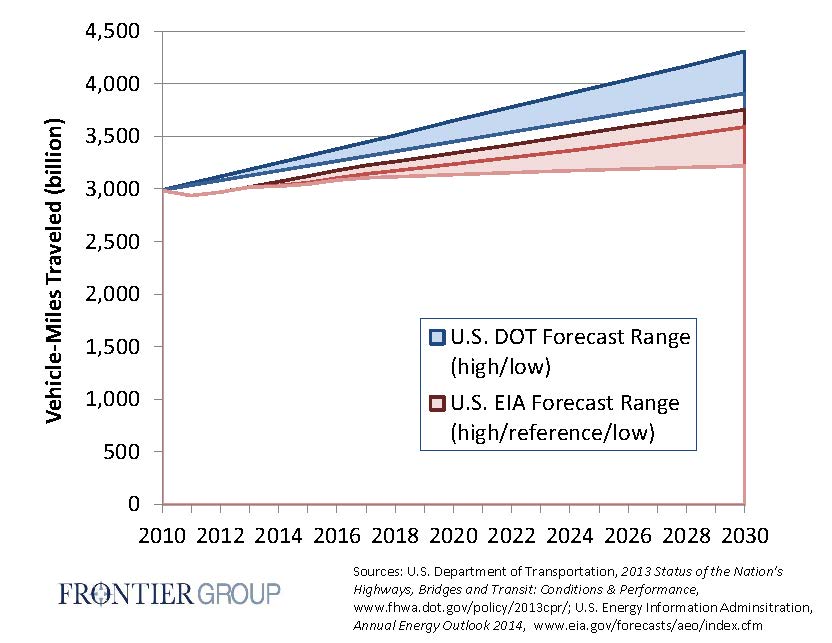
It also serves as a telling contrast to the U.S. Department of Transportation’s own recent forecast of vehicle travel, presented in the biennial "Conditions and Performance" report.
We’ve criticized the U.S. DOT before for regularly overshooting the mark when it comes to forecasting vehicle travel, exaggerating the need for spending on highway expansion and maintenance. The EIA report, on the other hand, takes a more nuanced and thoughtful approach to forecasting than the DOT’s reliance on untrustworthy state data and straight-line projections. It also gives us some key indications of what slower VMT growth might mean for our energy future.
DOT is from Mars, EIA is from Venus – Diverging Forecasts
The EIA and DOT have very different thoughts about how the future will play out when it comes to trends in driving. The DOT forecasts an immediate resumption of rates of vehicle travel growth that haven’t been seen for a decade, while the EIA assumes that, while driving might pick up again soon, it also might not, and that, to the extent driving does increase in the future, it is likely to grow way more slowly than it did during the post-war Driving Boom. This is the case we made in our 2013 report, A New Direction.
Incredibly, even the EIA’s “high VMT” case forecasts a level of driving that is below the DOT’s “low” forecast. One wonders how much of the $124 billion to $146 billion in annual expenditures the DOT says are needed to improve the conditions and performance of the highway system would still be necessary in the “low VMT” forecast put forward by the EIA. One also wonders how the EIA’s slow VMT growth forecast would affect revenues for the Highway Trust Fund, which is currently less than 150 days from going broke.
Slow VMT Growth Saves Oil and Cuts Pollution
The EIA report doesn’t give us the answer to those questions, but it does play out some of the other implications of reduced VMT growth, particularly with regard to oil consumption and carbon dioxide emissions. To follow are two charts from the EIA report – one showing the change in light-duty vehicle energy consumption under the various VMT scenarios and the other showing the change in transportation sector carbon dioxide emissions.
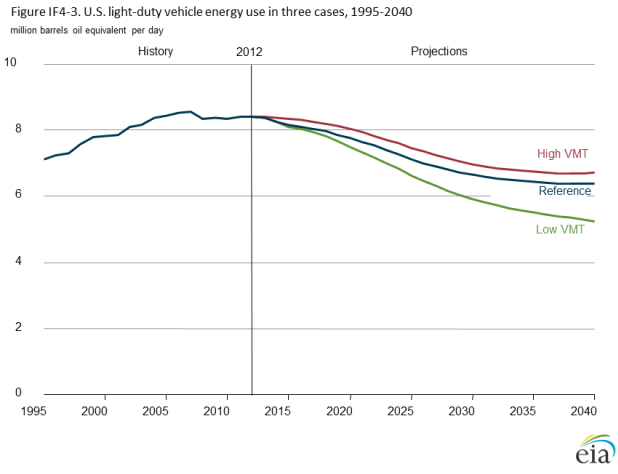
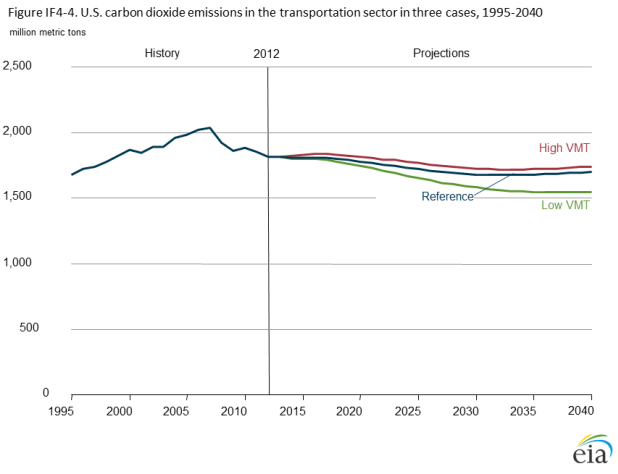
VMT growth in line with the “low VMT” scenario would cut energy use by U.S. light-duty vehicles by nearly one-fifth relative to the reference case and slash transportation sector carbon dioxide emissions by 9 percent. Slowing VMT growth, in other words, can help meet the urgent need to reduce emissions of global warming pollution and help put the nation on a pathway to a sustainable energy future that is less dependent on fossil fuels.
It is impossible to know, of course, whether the EIA or the DOT forecast will prove to be correct. But the new EIA report brings much-needed fresh thinking to the topic, and it also reminds us that, regardless of whether economic, demographic and other factors will continue to slow VMT growth, the nation has a lot to gain from using public policy to help the transition along.





